In today’s fast-paced world, mental health issues like depression, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) are increasingly prevalent. Traditional treatments, such as medication and psychotherapy, do not always provide relief for all patients, particularly those with treatment-resistant conditions. This gap highlights the necessity for alternative treatments that can offer effective solutions without the side effects often associated with pharmacological therapies. TMS therapy for mental health provides a promising alternative, leveraging non-invasive technology to directly enhance brain function and mood.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a revolutionary approach to treating mental health disorders. This technique uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain, specifically targeting areas involved in mood regulation. What is TMS therapy? Essentially, it is a procedure that involves placing an electromagnetic coil against the scalp near the forehead. The device then emits a magnetic pulse that stimulates brain cells, promoting changes in brain activity associated with mood improvement. This method is gaining traction as a safe and effective treatment for a variety of mental health conditions, particularly major depression.

How TMS Therapy Works
The Science Behind Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is based on the principles of electromagnetic induction, first discovered by Michael Faraday. When the TMS device is activated, it generates a magnetic field that rapidly changes intensity. This magnetic field penetrates the skull non-invasively and induces a small electric current in specific areas of the brain. This current stimulates neural activity in regions known to be underactive in conditions like depression. By activating these areas, TMS encourages the brain to reestablish normal activity patterns, which can alleviate symptoms of mental health disorders.
Targeting Brain Regions for Mood Regulation
The effectiveness of TMS therapy for depression largely depends on accurately targeting specific brain regions associated with mood regulation, primarily the prefrontal cortex. This area of the brain is crucial for managing emotional responses and decision-making processes. TMS strategically stimulates this region to improve mood and cognitive functions. The precise targeting is guided by neuroimaging techniques and individualized brain mapping to ensure optimal outcomes, making it a tailored therapy suited to the needs of each patient.
Non-Invasive Nature of TMS Therapy
One of the most significant advantages of TMS is its non-invasive nature. Unlike other brain stimulation treatments, such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), TMS treatment does not require anesthesia, and there are no systemic side effects typically associated with more invasive procedures. Patients undergoing TMS are awake and alert during the session, can immediately resume their daily activities post-treatment, and typically experience minimal discomfort, making TMS an appealing option for those wary of invasive procedures or concerned about the side effects of traditional treatments.
Comparison to Other Brain Stimulation Techniques
Comparatively, TMS is a gentler and less invasive alternative to other brain stimulation techniques. For instance, ECT, while effective for severe depression, often results in significant side effects, including memory loss and confusion. Another method, deep brain stimulation (DBS), requires surgical implantation of electrodes. In contrast, TMS for depression offers a balance between efficacy and safety, providing substantial relief with fewer cognitive side effects. This makes TMS particularly suitable for patients seeking effective treatment without the risks and recovery time associated with more invasive brain stimulation therapies.
TMS Therapy for Depression
TMS as an Advanced Treatment for Major Depression
TMS therapy for major depression represents a significant advancement in psychiatric care, offering a new horizon for patients who have not found relief through traditional treatments. The approach targets specific areas within the brain that are known to be underactive in depression, particularly the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. By stimulating these regions, TMS helps to elevate mood and alleviate the emotional and cognitive symptoms associated with major depression. This focused stimulation encourages the brain to reorganize the way it processes emotional information, which can lead to substantial improvements in how patients feel and function daily.
Effectiveness of TMS in Treatment-Resistant Depression
For those with treatment-resistant depression, TMS provides a beacon of hope. Numerous clinical trials and real-world studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of TMS treatment for depression in patients who have failed to respond to antidepressants or psychotherapy. TMS offers a novel approach by using magnetic fields to directly influence neuronal activity, bypassing the gastrointestinal system and avoiding the systemic side effects often associated with antidepressants. This direct brain modulation can jump-start neural activity in dormant areas, offering patients noticeable improvements often within weeks of starting treatment.
Improving Mood and Reducing Symptoms Through TMS
The goal of TMS therapy for depression is not only to alleviate the overt symptoms but also to improve overall quality of life for patients. This treatment helps to reduce the pervasive sadness, lethargy, and hopelessness often associated with depression and can also enhance cognitive functions like memory and concentration that are frequently impaired by the disorder. Patients undergoing TMS often report an increase in energy, better sleep patterns, and an improved ability to enjoy life’s activities—changes that can be transformative.
Protocol for TMS Sessions and Expected Outcomes
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is an innovative treatment that follows a structured protocol to help alleviate symptoms of depression. The process is designed to be both effective and minimally invasive, allowing patients to undergo treatment with minimal disruption to their daily lives.
- Session Duration and Frequency: Each TMS session typically lasts between 30 to 60 minutes. Patients usually attend these sessions five days a week, which helps to maintain the momentum of treatment and optimize outcomes.
- Treatment Setting: During a TMS session, the patient sits in a comfortable, reclining chair. This relaxed posture helps to ease any anxiety and ensures the patient remains still during the treatment to maximize the accuracy of the device placement.
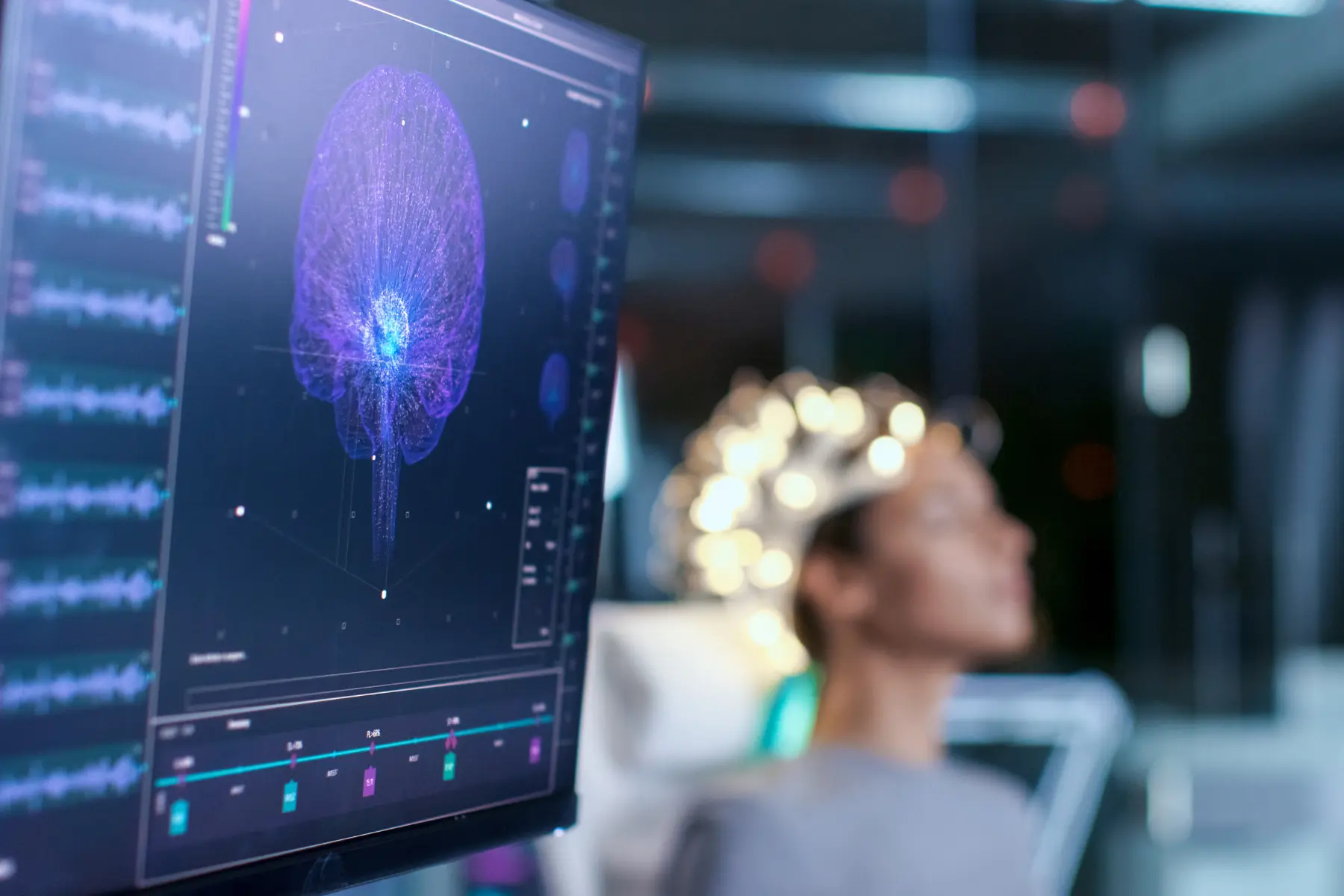
- Device Placement and Operation: A small, curved device, known as a TMS coil, is positioned on the patient’s head, specifically over the prefrontal cortex which is the region typically associated with mood regulation. This device generates focused electromagnetic pulses that penetrate the skull to stimulate brain cells.
- Experience During Treatment: The treatment is generally painless. Patients may feel a tapping sensation on their scalp and hear a clicking sound as the machine operates. These sensations are normal and indicate that the treatment is being administered correctly.
- Immediate Post-Session Activities: After a session, patients can immediately return to their normal daily activities. There is no need for recovery time, making it a convenient option for patients looking to integrate treatment into their regular schedule.
The expected outcomes from this structured approach include a gradual improvement in both mood and cognitive functions, typically starting to become noticeable in the second or third week of treatment. The consistency and frequency of the sessions contribute to these results, with the cumulative effect of regular sessions often leading to significant and lasting relief from depressive symptoms.
Expanding Applications of TMS Therapy
TMS for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
TMS therapy for anxiety is emerging as a beneficial treatment for individuals suffering from generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). By targeting the brain’s prefrontal cortex, TMS helps to regulate the excessive worry and tension characteristic of GAD, reducing the hyperactivity in areas that are often overstimulated in anxious individuals. This modulation helps patients achieve a calmer state of mind and decreases the physical symptoms of anxiety, such as restlessness and rapid heartbeat, providing a non-pharmacological option that avoids the side effects of traditional anxiety medications.
TMS Therapy for Panic Disorders
TMS also shows promise in treating panic disorders, a condition marked by sudden, intense bouts of fear or discomfort. By focusing magnetic stimulation on specific areas of the brain associated with fear response, TMS can help reduce the frequency and severity of panic attacks. This treatment modality offers a new hope for patients who might not respond well to psychotherapy alone or who wish to avoid the long-term use of anti-anxiety drugs. TMS provides a rapid response to treatment, which is crucial for patients seeking immediate relief from the debilitating effects of panic disorders.
TMS in the Treatment of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
The application of TMS in the treatment of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) represents another innovative use of this technology. OCD is characterized by unwanted and intrusive thoughts that trigger anxiety, followed by repetitive behaviors aimed at reducing this anxiety. TMS therapy targets the neural circuits involved in controlling these compulsive behaviors and the accompanying anxiety. By adjusting the activity levels in these circuits, TMS can help alleviate the compulsions and obsessions associated with OCD, leading to significant improvements in daily functioning and overall quality of life.
Potential Future Uses of TMS in Mental Health
Looking forward, the potential applications of TMS therapy are broad and promising. Ongoing research is exploring the use of TMS for a variety of other mental health conditions, including but not limited to addiction, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and chronic pain, each of which involves distinct brain regions that can potentially be modulated by magnetic stimulation. As our understanding of the brain’s functioning in these disorders deepens, TMS could become an integral part of a more personalized approach to mental health treatment, tailored to the specific neural needs of individual patients.

Benefits of TMS Therapy for Mental Health Conditions
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) provides distinct advantages over traditional pharmacological treatments for mental health conditions, particularly in its method of action and the side effects profile. These advantages make TMS a compelling alternative for patients seeking effective treatment without the complications often associated with medications.
- Elimination of Pharmacokinetic Variables: TMS bypasses the digestive system and liver, eliminating the pharmacokinetic issues such as absorption rates and metabolic differences that can significantly affect the efficacy of oral medications. This direct approach allows for more consistent and predictable therapeutic effects.
- No Systemic Side Effects: Unlike traditional antidepressants, which can affect the entire body and lead to a range of side effects like gastrointestinal upset, weight gain, and sexual dysfunction, TMS targets specific areas of the brain. This localized treatment reduces the likelihood of systemic side effects, offering a cleaner alternative to managing mental health.
- Avoidance of Emotional Numbing: Patients often report that certain antidepressants can lead to emotional numbing, where they feel less like themselves. TMS, however, stimulates brain activity without altering the brain’s chemical balance, preserving patients’ emotional sensitivity.
- Targeted Neuronal Activation: TMS specifically enhances activity in areas of the brain associated with mood regulation and cognitive function. This targeted activation helps to improve symptoms related to mental health conditions without disrupting other brain areas or bodily functions.
- Reduction in Treatment Variability: By directly stimulating the brain, TMS reduces the variability often seen in response to pharmacological treatments, which can be influenced by factors like age, diet, and other medications. This makes TMS a more reliable and effective treatment option.
These attributes of TMS therapy highlight its position as a modern, efficient, and patient-friendly approach to treating mental health issues. As TMS continues to gain recognition and become more accessible, it is likely to offer a valuable treatment option for patients who have not had success with traditional pharmacological approaches or who seek a treatment with fewer side effects and complications.
No Requirement for Anesthesia or Hospitalization
TMS therapy does not require anesthesia, sedation, or any form of hospitalization, distinguishing it sharply from other forms of brain stimulation treatments that require more intensive medical oversight. Patients can walk into a clinic, receive treatment, and resume their daily activities almost immediately without the need for recovery time. This aspect of TMS not only makes it more accessible and less daunting for patients but also reduces the overall cost and complexity of the treatment process.
Criteria for TMS Therapy Candidates
Identifying Suitable Candidates for TMS Therapy
Determining who is a suitable candidate for TMS therapy involves a comprehensive evaluation process. Ideal candidates are typically those who have not responded adequately to traditional antidepressants or who experience intolerable side effects from medications. The evaluation includes a detailed medical history, a review of psychiatric symptoms, and often a physical examination to rule out any neurological conditions that could influence the effectiveness or safety of TMS. Mental health professionals also consider factors such as the severity and duration of depressive episodes, ensuring that TMS is a fit for the individual’s specific needs.
Patient Screening and Evaluation Processes
The screening process for TMS treatment is thorough and designed to ensure maximum safety and efficacy. It often includes psychiatric assessments to confirm the diagnosis of depression or other treatable conditions under TMS protocols. Additionally, patients undergo a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan to map brain structure for precise targeting during treatment. Screening also helps to identify any contraindications, such as the presence of metal implants or other medical devices that could interact negatively with magnetic fields, ensuring that TMS is administered safely.
Customizing TMS Protocols for Individual Needs
Once a patient is deemed a suitable candidate, TMS protocols are customized to match their individual needs. This customization involves adjusting the intensity of the magnetic pulses and the specific brain regions targeted during treatment. The process is guided by initial evaluations and ongoing monitoring of patient responses, allowing for adjustments in real-time based on individual progress and tolerance to the treatment. This personalized approach helps maximize the therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential side effects, making TMS a highly adaptive treatment option.
The Role of TMS Clinics in Providing Care
TMS clinics play a crucial role in the administration of TMS therapy. These specialized facilities are equipped with the latest TMS technology and staffed by trained professionals who oversee the treatment process. Clinics provide a controlled environment where safety protocols are rigorously followed, and patient comfort is prioritized. The clinical setting also facilitates an integrated approach to care, where psychiatric support and counseling are available to complement the TMS treatment, ensuring a holistic approach to mental health recovery.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is gaining increasing recognition as a forefront treatment for a variety of mental health conditions beyond just depression. Its ability to non-invasively stimulate the brain and promote neurological health makes TMS advanced depression therapy a pioneering approach in the field.
Looking ahead, the future of TMS therapy in mental health treatment appears promising. As research continues to evolve, the potential applications of TMS are expanding, promising new treatment possibilities for conditions that are currently difficult to manage. Innovations in technology and technique are expected to enhance the efficacy and accessibility of TMS, making it possible to tailor treatments even more closely to individual patient needs. This progression will likely cement TMS’s role as one of the best TMS therapy options available, characterized by its minimal side effects, non-invasive nature, and rapid effectiveness.

The advancements in TMS technology and methodology underscore its potential as a transformative tool in mental health care. As what is TMS depression therapy becomes more commonly understood, the stigma around such treatments decreases, paving the way for more individuals to seek out this effective alternative. The integration of TMS into mainstream treatment options represents a significant shift towards more personalized and advanced healthcare solutions, promising better outcomes for patients with mental health disorders.